The Algebraic and Geometric Proofs of Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that if a right triangle has side lengths  and
and  , and that
, and that  is its hypotenuse (longest side), then the sum of the squares of the two shorter side lengths is equal to the square of the length of its hypotenuse.
is its hypotenuse (longest side), then the sum of the squares of the two shorter side lengths is equal to the square of the length of its hypotenuse.
Putting it in equation form, following the abovementioned conditions, the following relationship holds:
For example, if a right triangle has side lengths 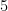 and
and 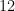 , then the length of its hypotenuse is
, then the length of its hypotenuse is 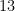 , since
, since 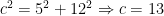 .
.
Exercise 1: What is the hypotenuse of the triangle with sides  and
and  ?
?
The converse of the theorem is also true. If the side lengths of the triangle satisfy the equation 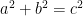 , then the triangle is right. For instance, a triangle with side lengths
, then the triangle is right. For instance, a triangle with side lengths 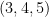 satisfies the equation
satisfies the equation 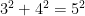 , therefore, the said triangle is right.
, therefore, the said triangle is right.
Geometrically speaking, the Pythagorean theorem states that if you have a right triangle with sides  and
and  (
( being the hypotenuse), and you constructed three squares containing the sides of the triangle as shown in Figure 2, the area of the two smaller squares when added equals the area of the largest square (click here to see animation).
being the hypotenuse), and you constructed three squares containing the sides of the triangle as shown in Figure 2, the area of the two smaller squares when added equals the area of the largest square (click here to see animation).

Figure 2 – The geometric interpretation of the Pythagorean theoremstates that the area of the green square plus the area of the red square is equal to the area of the blue square.
One specific case is shown in Figure 3: the areas of the two smaller squares are 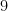 and
and  square units, and the area of the largest square is
square units, and the area of the largest square is  square units.
square units.
Exercise 2: Verify that the area of the largest square in Figure 3 is 25 square units.
Similarly, triangles with side lengths 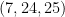 and
and 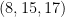 are right triangles. If the side lengths of a right triangle are all integers, we call themPythagorean triple. Hence,
are right triangles. If the side lengths of a right triangle are all integers, we call themPythagorean triple. Hence, 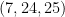 and
and 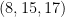 are Pythagorean triples.
are Pythagorean triples.
Exercise 3: Give other examples of Pythagorean triples.
Exercise 4: Prove that there are infinitely many Pythagorean triples.
Proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem
There are more than 300 proofs of the Pythagorean theorem. More than 70 proofs shown in Cut-The-Knot website. Shown below are two of the proofs. Note that in proving the Pythagorean theorem, we want to show that for any right triangle with hypotenuse  , and sides
, and sides  , and
, and 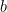 , the following relationship holds:
, the following relationship holds: 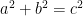 .
.
Geometric Proof
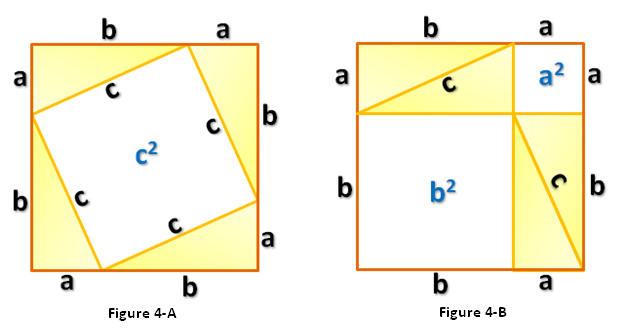
First, we draw a triangle with side lengths  and
and  as shown in Figure 1. Next, create 4 triangles identical to it and using the triangles form a square with side lengths
as shown in Figure 1. Next, create 4 triangles identical to it and using the triangles form a square with side lengths 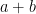 as shown in Figure 4-A. Notice that the area of the white square in Figure 4-A is
as shown in Figure 4-A. Notice that the area of the white square in Figure 4-A is 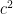 .
.
Rearranging the triangles, we can also form another square with the same side length as shown in Figure 4-B.This means that the area of the white square in the Figure 4-A is equal to the sum of the areas of the white squares in Figure 4-B (Why?). That is, 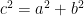 which is exactly what we want to show. *And since we can always form a (big) square using four right triangles with any dimension (in higher mathematics, we say that we can choose arbitrary
which is exactly what we want to show. *And since we can always form a (big) square using four right triangles with any dimension (in higher mathematics, we say that we can choose arbitrary  and
and 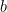 as side lengths of a right triangle), this implies that the equation
as side lengths of a right triangle), this implies that the equation 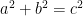 stated above is always true.
stated above is always true.
Exercise 5: Prove that the quadrilateral with side length C in Figure 4-A is a square.
Algebraic Proof
Method 1: 
Method 2: 
Methods 1 and 2 calculated the area of the same square, therefore they must be equal. This means that we can equate both expressions. Equating we have,
which is exactly what we want to show.
 1:37 AM
1:37 AM
 Muhammad Yusuf
, Posted in
Muhammad Yusuf
, Posted in



















0 Response to "The Algebraic and Geometric Proofs of Pythagorean Theorem"
Post a Comment